The breadth of online collaborative tools that are emerging today is quite simply staggering! A number of websites have appeared offering specific product offerings, or hosting a multitude of collaborative tools (wiki's, blogs, forums, repositories, communication tools etc.) from which to work. What is so promising is the versatility and sophistication of products such as Thinkfold and Mindmeister, with niche products serving every kind of need imaginable. Crucially, many of these tools now offer real-time co-editing of documents (changes appear in real-time for all users), multiple user capability, rich timeline of changes and additional communication tools etc.
In the near future, we will likely see some consolidation and more compatibility amongst these products, as well as platforms which (on the fly) integrate tools into a single collaborative online environment from which to work.
In the meantime, Robin good , a social media guru, has put together a continually updated mindmap of online collaborative tools currently available at; http://www.mindmeister.com/maps/show_public/12213323 . The map offers an impressive list broken down by category of sites offering collaborative tools. They really are worth checking out!!
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Tuesday, May 26, 2009
Monday, May 25, 2009
Searching on the web; the new breed of search engines
There has been alot of talk recently (on the web and elsewhere) about the next generation of "smarter" search engines. Below are examples of search engines which have recently gained coverage over their ability to either (1) structure and present data pulled from the web, (2) assign semantic filtering by quality, (3) search structured data on the web, (4) search the 'real-time' web or (5) search the 'deep web':
(1) Structure and present data pulled from the web
Wolfram Alpha
'We aim to collect and curate all objective data; implement every known model, method, and algorithm; and make it possible to compute whatever can be computed about anything. Our goal is to build on the achievements of science and other systematizations of knowledge to provide a single source that can be relied on by everyone for definitive answers to factual queries.' (Wolfram, 2009) http://www.wolframalpha.com/
Google Squared
'Google Squared doesn't find webpages about your topic — instead, it automatically fetches and organizes facts from across the Internet.' (Google, 2009) It extracts data from relevant webpages and presents them in squared frames on a results page.
http://squared.google.com/
Bing
Bing is built to 'go beyond today's search experience' through recognising content and adapting to your query types, providing results which are "decision driven". According to the company; "we set out to create a new type of search experience with improvements in three key areas: (1) Delivering great search results and one-click access to relevant information, (2) Creating a more organized search experience, (3) Simplifying tasks and providing tools that enable insight about key decisions." (Microsoft, 2009)
http://www.bing.com/
http://www.discoverbing.com/
Sensebot
'SenseBot delivers a summary in response to your search query instead of a collection of links to Web pages. SenseBot parses results from the Web and prepares a text summary of them. The summary serves as a digest on the topic of your query, blending together the most significant and relevant aspects of the search results. The summary itself becomes the main result of your search...Sensebot attempts to understand what the result pages are about. It uses text mining to parse Web pages and identify their key semantic concepts. It then performs multidocument summarization of content to produce a coherent summary' (Sensebot, 2008)
http://www.sensebot.net/
(2) Provide more semantic filtering of information by quality
Hakia
'Hakia’s semantic technology provides a new search experience that is focused on quality, not popularity. hakia’s quality search results satisfy three criteria simultaneously: They (1) come from credible Web sites recommended by librarians, (2) represent the most recent information available, and (3) remain absolutely relevant to the query' (Hakia, 2009)
http://www.hakia.com/
(3) Search structured data on the web
SWSE
' There is already a lot of data out there which conforms to the proposed SW standards (e.g. RDF and OWL). Small vertical vocabularies and ontologies have emerged, and the community of people using these is growing daily. People publish descriptions about themselves using FOAF (Friend of a Friend), news providers publish newsfeeds in RSS (RDF Site Summary), and pictures are being annotated using various RDF vocabularies. [SWSE is] service which continuously explores and indexes the Semantic Web and provides an easy-to-use interface through which users can find the data they are looking for. We are therefore developing a Semantic Web Search Engine' (SWSE, 2009)
http://swse.deri.org/
Swoogle
'Swoogle is a search engine for the Semantic Web on the Web. Swoogle crawl the World Wide Web for a special class of web documents called Semantic Web documents, which are written in RDF' (Swoogle, 2007)
http://swoogle.umbc.edu/
Similar offering is;
http://watson.kmi.open.ac.uk/WatsonWUI/
(4) Search the 'real-time' web
One Riot
'OneRiot crawls the links people share on Twitter, Digg and other social sharing services, then indexes the content on those pages in seconds. The end result is a search experience that allows users to find the freshest, most socially-relevant content from across the realtime web....we index our search results according to their current relevance and popularity' (Oneriot, 2009)
http://www.oneriot.com/
Scoopler
'Scoopler is a real-time search engine. We aggregate and organize content being shared on the internet as it happens, like eye-witness reports of breaking news, photos and videos from big events, and links to the hottest memes of the day. We do this by constantly indexing live updates from services including Twitter, Flickr, Digg, Delicious and more.' (Scoopler, 2009)
http://www.scoopler.com/
Collecta
'Collecta monitors the update streams of news sites, popular blogs and social media, and Flickr, so we can show you results as they happen' (Collecta. 2009).
http://www.collecta.com/
(5) Search the 'deep web'
DeepDyve
'The DeepDyve research engine uses proprietary search and indexing technology to cull rich, relevant content from thousands of journals, millions of documents, and billions of untapped Deep Web pages.' 'Researchers, students, technical professionals, business users, and other information consumers can access a wealth of untapped information that resides on the "Deep Web" – the vast majority of the Internet that is not indexed by traditional, consumer-based search engines. The DeepDyve research engine unlocks this in-depth, professional content and returns results that are not cluttered by opinion sites and irrelevant content.... The KeyPhrase™ algorithm, applies indexing techniques from the field of genomics. The algorithm matches patterns and symbols on a scale that traditional search engines cannot match, and it is perfectly suited for complex data found on the Deep Web' (Deepdyve, 2009)
http://www.deepdyve.com/
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
(1) Structure and present data pulled from the web
Wolfram Alpha
'We aim to collect and curate all objective data; implement every known model, method, and algorithm; and make it possible to compute whatever can be computed about anything. Our goal is to build on the achievements of science and other systematizations of knowledge to provide a single source that can be relied on by everyone for definitive answers to factual queries.' (Wolfram, 2009) http://www.wolframalpha.com/
Google Squared
'Google Squared doesn't find webpages about your topic — instead, it automatically fetches and organizes facts from across the Internet.' (Google, 2009) It extracts data from relevant webpages and presents them in squared frames on a results page.
http://squared.google.com/
Bing
Bing is built to 'go beyond today's search experience' through recognising content and adapting to your query types, providing results which are "decision driven". According to the company; "we set out to create a new type of search experience with improvements in three key areas: (1) Delivering great search results and one-click access to relevant information, (2) Creating a more organized search experience, (3) Simplifying tasks and providing tools that enable insight about key decisions." (Microsoft, 2009)
http://www.bing.com/
http://www.discoverbing.com/
Sensebot
'SenseBot delivers a summary in response to your search query instead of a collection of links to Web pages. SenseBot parses results from the Web and prepares a text summary of them. The summary serves as a digest on the topic of your query, blending together the most significant and relevant aspects of the search results. The summary itself becomes the main result of your search...Sensebot attempts to understand what the result pages are about. It uses text mining to parse Web pages and identify their key semantic concepts. It then performs multidocument summarization of content to produce a coherent summary' (Sensebot, 2008)
http://www.sensebot.net/
(2) Provide more semantic filtering of information by quality
Hakia
'Hakia’s semantic technology provides a new search experience that is focused on quality, not popularity. hakia’s quality search results satisfy three criteria simultaneously: They (1) come from credible Web sites recommended by librarians, (2) represent the most recent information available, and (3) remain absolutely relevant to the query' (Hakia, 2009)
http://www.hakia.com/
(3) Search structured data on the web
SWSE
' There is already a lot of data out there which conforms to the proposed SW standards (e.g. RDF and OWL). Small vertical vocabularies and ontologies have emerged, and the community of people using these is growing daily. People publish descriptions about themselves using FOAF (Friend of a Friend), news providers publish newsfeeds in RSS (RDF Site Summary), and pictures are being annotated using various RDF vocabularies. [SWSE is] service which continuously explores and indexes the Semantic Web and provides an easy-to-use interface through which users can find the data they are looking for. We are therefore developing a Semantic Web Search Engine' (SWSE, 2009)
http://swse.deri.org/
Swoogle
'Swoogle is a search engine for the Semantic Web on the Web. Swoogle crawl the World Wide Web for a special class of web documents called Semantic Web documents, which are written in RDF' (Swoogle, 2007)
http://swoogle.umbc.edu/
Similar offering is;
http://watson.kmi.open.ac.uk/WatsonWUI/
(4) Search the 'real-time' web
One Riot
'OneRiot crawls the links people share on Twitter, Digg and other social sharing services, then indexes the content on those pages in seconds. The end result is a search experience that allows users to find the freshest, most socially-relevant content from across the realtime web....we index our search results according to their current relevance and popularity' (Oneriot, 2009)
http://www.oneriot.com/
Scoopler
'Scoopler is a real-time search engine. We aggregate and organize content being shared on the internet as it happens, like eye-witness reports of breaking news, photos and videos from big events, and links to the hottest memes of the day. We do this by constantly indexing live updates from services including Twitter, Flickr, Digg, Delicious and more.' (Scoopler, 2009)
http://www.scoopler.com/
Collecta
'Collecta monitors the update streams of news sites, popular blogs and social media, and Flickr, so we can show you results as they happen' (Collecta. 2009).
http://www.collecta.com/
(5) Search the 'deep web'
DeepDyve
'The DeepDyve research engine uses proprietary search and indexing technology to cull rich, relevant content from thousands of journals, millions of documents, and billions of untapped Deep Web pages.' 'Researchers, students, technical professionals, business users, and other information consumers can access a wealth of untapped information that resides on the "Deep Web" – the vast majority of the Internet that is not indexed by traditional, consumer-based search engines. The DeepDyve research engine unlocks this in-depth, professional content and returns results that are not cluttered by opinion sites and irrelevant content.... The KeyPhrase™ algorithm, applies indexing techniques from the field of genomics. The algorithm matches patterns and symbols on a scale that traditional search engines cannot match, and it is perfectly suited for complex data found on the Deep Web' (Deepdyve, 2009)
http://www.deepdyve.com/
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Monday, May 18, 2009
How to personalise images for illuminous desktop wallpaper
Here is my 'how to' for personalising the winning shot of the 'International Garden photo' competition over at Igpoty . The results should make some illuminous desktop wallpaper for your computer.
1. Open the following image (available at Igpoty ) in Photoshop :
2. Use the lasso tool to mark out and highlight the sky (3 pieces). You'll need to copy each piece separately, then paste to a new layer
3. When all layers are copied. Merge them them until you have 1 piece.
4. Next use the lasso tool to mark out and copy the girl. Paste to a new layer. Do the same for the rock.
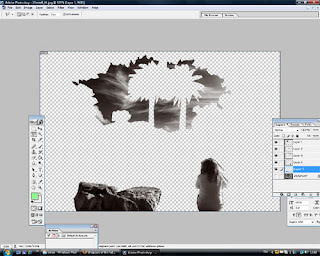
5. You should now have 3 additional layers on top of the original. If you hide the original layer, you should see the following;
8. Finally, if you like, you can add additional effects such as rendering a 'Lens flare':
9. You may want to enlarge the original image to the resolution of your desktop before saving.
10. Choose 'save for web' and save as a Jpeg image.
11. And thats it, you should have a terrific personalised desktop wallpaper or screensaver.
Here is a link to download 1200x1800 resolution images of the examples above;
http://rapidshare.com/files/234404204/screensavers.zip.html
Copyright © 2009 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
1. Open the following image (available at Igpoty ) in Photoshop :
2. Use the lasso tool to mark out and highlight the sky (3 pieces). You'll need to copy each piece separately, then paste to a new layer
3. When all layers are copied. Merge them them until you have 1 piece.
4. Next use the lasso tool to mark out and copy the girl. Paste to a new layer. Do the same for the rock.
5. You should now have 3 additional layers on top of the original. If you hide the original layer, you should see the following;
6. You can now very lightly feather these new layers (1px or 2px max) so that they will eventually blend better with the original layer.
7. Use the 'Gradient Map' in 'Adjustments' to create a gradient of colours for both the original layer and the 'sky' layer. Below are example's of the finished product:
8. Finally, if you like, you can add additional effects such as rendering a 'Lens flare':
9. You may want to enlarge the original image to the resolution of your desktop before saving.
10. Choose 'save for web' and save as a Jpeg image.
11. And thats it, you should have a terrific personalised desktop wallpaper or screensaver.
Here is a link to download 1200x1800 resolution images of the examples above;
http://rapidshare.com/files/234404204/screensavers.zip.html
Copyright © 2009 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Labels:
background,
desktop,
howto,
personalise,
photoshop,
wallpaper
Sunday, March 22, 2009
Friday, March 13, 2009
Twitter and it's data free for all....
The rise of Twitter
Twitter is expanding and expanding fast. A flurry of news coverage and hype about the product, particularly in the last 3 months, has seen users flock to the service. Twitter is seen to offer enormous potential, information can be filtered by content, location, keyword etc., opening up the realms of how data is used online in real time. This is in tandem with the numerous benefits of openness discussed below. However, Twitter still has some way to go. It has yet to come to terms with its own potential and how those possibilities should be steered and constrained. The service recently made some small developments to its site, with a 'trend' and 'search' facility added. However, the sophistication of its privacy and account settings is still limited. Thus, it has yet to put more control back in users hand, with regard to how their data is used and by whom. At present, it is an all or nothing affair, you're "open" or you're "private"!!. This begs the following questions, should account holders have more control over their data? If so, why should this be the case? Is openness itself constraining what people will say? Finally, If users have more control, will this stifle the success of the service?
Why openness?
The Twitter model is built largely around individuals posting short 140 character status updates, replies or retweets on any range of topic imaginable. Individuals can find and follow any other user on the service, ranging from friends to common interests, to celebrities etc. The great thing about twitter is its 'openness'. Most individuals choose to keep their profile public to ensure that they can be found by like-minded individuals, or that ongoing conversations can be picked up by interested parties etc. It means individuals have that feeling that someone out there is listening, even if it is just the possibility of feeling part of something. It is a forum for expression of the mind, even if expression is mundane. It is also a means to 'contribute' one's time, knowledge and experience and is thus an avenue of 'meaning' for individuals.
Openness ensures that those with something to offer others can more easily be heard. It engenders the possibility for more connection, collaboration, relationship and even community formation 'without' boundaries. By focusing on the content of messages and less on the full personality, it provides a different kind of social formation. The loud, influential and dominant personality may not make for interesting dialogue. Too many annoying tweets from a user and one can easily unfollow with the click of the mouse. This levels the playing field for users in many respects, as well as increasing the possibility of connection based on interest and not by persuasion. However, not everyone wishes for this openness. There is the option to set your profile 'private' in order to close your information to only those with whom you've allowed follow you.
Interpreting your past online
Full openness has its price though, Twitter first launched in March 2006, and since then, an archive of user data has slowly being amounting for all to access. Hundreds of your messages may (or may not) be carefully vetted by you, but one thoughtless twitter update may be enough to get you in to trouble at any point in the future. This may be nothing more than friends misinterpreting and taking offence to an update. But it could be something more: Recently a US cop had his status updates on Facebook and Myspace used as evidence against him in a gun trial on grounds of the accused acquittal. What was interesting about this case is how status updates became utilised and crucially 'interpreted' by the Jury. This highlights how information may be interpreted and placed into multiple contexts by whoever reads the information. Employers, even potential collaborators, may selectively choose just one suspect twitter update among hundreds as 'proof' of character, or misintrepret one's online ego as holistically representative of the individual. Twitter means your online past and identity will always be there online, waiting to be interpreted and analysed.
Analyse this!
You may think that with hundreds of recorded messages, it would be uncumbersome for anyone to want to thrall through your past data. But with twitter, software by third parties is springing up to offer just that: Twitter analyzer is just one of the free online applications available that allows you to analyse the data of "any" twitter user with an open account (hence the majority of twitter user). The bounds of what can be achieved with Twitter analyzer is limited. But it opens numerous possibilities. For beyond harmless apps like Twitscoop, which scrape status updates in order to form twitter 'trending topics' and 'buzz words', your data can be analysed in isolation or in tandem with others, in any number of ways, for any number of purposes, and by ANYONE. Twitter apps may emerge (if they don't already exist) to 'profile' individuals; to elucidate personality, truth and inconsistency, track record, literacy, interests etc. etc. etc. This is alongside the likely emergence of targeted advertising etc, and data mining of information, in order to make twitter a viable business model.
Openness on whose terms?
At present twitter has a very lax attitude to its data. If you have your profile public, your data is a free for all. If it's private, its between you, your vetted followers and twitter. This means that Twitter's so called openness may not be so open. People are constantly vetting and reflecting on what information they post on twitter. They may do it out of shyness, cautiousness, personal branding, or foresight etc. Twitter is open for many, but not too open. It's very openness curtails what dialogue does occur online. As users become aware of the ways in which their data can be used, this may further curtail individual expression. Thus, should Twitter not increase the range of choices with regard 'openness' and 'privacy'. What I would like to see is the possibility of users having the choice to make private their archive of data. For instance, what if only your recent updates were set as public? What if twitter made it difficult for those updates to be scraped by third party offerings? What if you could make replies only visible to who you follow? What if you could automatically make messages with certain 'keywords' private? What if you could make certain messages time sensitive and private after a certain period? What if you could make some status updates private to yourself? Thus, the bounds of privacy can be opened up. Will it constrain the services success however? I do not believe so, if too much openness is stifling expression and conversation on twitter, than increasing the scope of openness versus privacy, and doing it in an uncumbersome way; would perhaps increase use of the service. This choice may be the business model Twitter hopes for...
Copyright © 2009 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Twitter is expanding and expanding fast. A flurry of news coverage and hype about the product, particularly in the last 3 months, has seen users flock to the service. Twitter is seen to offer enormous potential, information can be filtered by content, location, keyword etc., opening up the realms of how data is used online in real time. This is in tandem with the numerous benefits of openness discussed below. However, Twitter still has some way to go. It has yet to come to terms with its own potential and how those possibilities should be steered and constrained. The service recently made some small developments to its site, with a 'trend' and 'search' facility added. However, the sophistication of its privacy and account settings is still limited. Thus, it has yet to put more control back in users hand, with regard to how their data is used and by whom. At present, it is an all or nothing affair, you're "open" or you're "private"!!. This begs the following questions, should account holders have more control over their data? If so, why should this be the case? Is openness itself constraining what people will say? Finally, If users have more control, will this stifle the success of the service?
Why openness?
The Twitter model is built largely around individuals posting short 140 character status updates, replies or retweets on any range of topic imaginable. Individuals can find and follow any other user on the service, ranging from friends to common interests, to celebrities etc. The great thing about twitter is its 'openness'. Most individuals choose to keep their profile public to ensure that they can be found by like-minded individuals, or that ongoing conversations can be picked up by interested parties etc. It means individuals have that feeling that someone out there is listening, even if it is just the possibility of feeling part of something. It is a forum for expression of the mind, even if expression is mundane. It is also a means to 'contribute' one's time, knowledge and experience and is thus an avenue of 'meaning' for individuals.
Openness ensures that those with something to offer others can more easily be heard. It engenders the possibility for more connection, collaboration, relationship and even community formation 'without' boundaries. By focusing on the content of messages and less on the full personality, it provides a different kind of social formation. The loud, influential and dominant personality may not make for interesting dialogue. Too many annoying tweets from a user and one can easily unfollow with the click of the mouse. This levels the playing field for users in many respects, as well as increasing the possibility of connection based on interest and not by persuasion. However, not everyone wishes for this openness. There is the option to set your profile 'private' in order to close your information to only those with whom you've allowed follow you.
Interpreting your past online
Full openness has its price though, Twitter first launched in March 2006, and since then, an archive of user data has slowly being amounting for all to access. Hundreds of your messages may (or may not) be carefully vetted by you, but one thoughtless twitter update may be enough to get you in to trouble at any point in the future. This may be nothing more than friends misinterpreting and taking offence to an update. But it could be something more: Recently a US cop had his status updates on Facebook and Myspace used as evidence against him in a gun trial on grounds of the accused acquittal. What was interesting about this case is how status updates became utilised and crucially 'interpreted' by the Jury. This highlights how information may be interpreted and placed into multiple contexts by whoever reads the information. Employers, even potential collaborators, may selectively choose just one suspect twitter update among hundreds as 'proof' of character, or misintrepret one's online ego as holistically representative of the individual. Twitter means your online past and identity will always be there online, waiting to be interpreted and analysed.
Analyse this!
You may think that with hundreds of recorded messages, it would be uncumbersome for anyone to want to thrall through your past data. But with twitter, software by third parties is springing up to offer just that: Twitter analyzer is just one of the free online applications available that allows you to analyse the data of "any" twitter user with an open account (hence the majority of twitter user). The bounds of what can be achieved with Twitter analyzer is limited. But it opens numerous possibilities. For beyond harmless apps like Twitscoop, which scrape status updates in order to form twitter 'trending topics' and 'buzz words', your data can be analysed in isolation or in tandem with others, in any number of ways, for any number of purposes, and by ANYONE. Twitter apps may emerge (if they don't already exist) to 'profile' individuals; to elucidate personality, truth and inconsistency, track record, literacy, interests etc. etc. etc. This is alongside the likely emergence of targeted advertising etc, and data mining of information, in order to make twitter a viable business model.
Openness on whose terms?
At present twitter has a very lax attitude to its data. If you have your profile public, your data is a free for all. If it's private, its between you, your vetted followers and twitter. This means that Twitter's so called openness may not be so open. People are constantly vetting and reflecting on what information they post on twitter. They may do it out of shyness, cautiousness, personal branding, or foresight etc. Twitter is open for many, but not too open. It's very openness curtails what dialogue does occur online. As users become aware of the ways in which their data can be used, this may further curtail individual expression. Thus, should Twitter not increase the range of choices with regard 'openness' and 'privacy'. What I would like to see is the possibility of users having the choice to make private their archive of data. For instance, what if only your recent updates were set as public? What if twitter made it difficult for those updates to be scraped by third party offerings? What if you could make replies only visible to who you follow? What if you could automatically make messages with certain 'keywords' private? What if you could make certain messages time sensitive and private after a certain period? What if you could make some status updates private to yourself? Thus, the bounds of privacy can be opened up. Will it constrain the services success however? I do not believe so, if too much openness is stifling expression and conversation on twitter, than increasing the scope of openness versus privacy, and doing it in an uncumbersome way; would perhaps increase use of the service. This choice may be the business model Twitter hopes for...
Copyright © 2009 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Labels:
analysis,
blog,
business model,
data,
data protection,
openness,
opinion,
privacy,
social media,
Twitter,
web 2.0
Monday, February 16, 2009
It's my data not yours!
Like many of you, I've been using 'web 2.0' sites for some time now. My use of them seems to be increasing and expanding of late. They allow someone like myself, who spends alot of time stuck in front of a computer, to maintain some degree of social interaction, express my interests and thus hold my sanity at bay.
In fact, I've come to like these new online offerings so much, that I want to do more!! For instance, I've been playing around with the idea of keeping an online journal for some time now. Having chosen a service that I liked; 'Penzu' , I realised that after keeping entries for more than a week, I had no assurance as to the integrity and access to data in the event of this service ceasing. The site gave no assurance about data portability or policy with regard to cessation of service. Then, I came across this interesting article by Bill Thompson over at the BBC See article: http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/technology/7760528.stm
He rightly raised the issue of data portability concluding that web site developers should do more. (Data Portability concerns the ability for user data to be transferred to another service, or downloaded by the user.) However I think he failed to fully argue what should be done about this issue. For example, if your data and/or intellectual property resides on a free online site, and that service changes its offering; is it made transparent and simple if you decide to jump ship to another offering? If your data and/or intellectual property resides on an online website and that website goes bust, will your data be kept safe and retrievable?
We already have some national government policies in place concerning the protection, control and privacy of data to individuals. However, I feel it should also be up to government to protect citizens with regard to movement, ownership and integrity of user data. For instance, more needs to be done to ensure that website owners have a required responsibility from the outset; to provide data portability and maintain this ability even after termination of service. Perhaps, this would require that the government step in and provide servers to back up user data in the event of a company ceasing. This could be in tandem with services (new or old) being required to ensure data integrity in the case of termination of service etc. Issues like ownership of data also needs to be addressed.
It is often argued that government should not inhibit the market, but I argue that the government should steer the market, maximising the longterm interests of it's citizens. Thus, I don't see a problem with positive interference in the market. The role of government is afterall to balance the realms of life. This is in view of citizens becoming increasingly reliant on the market, and thus, on online commercial offerings to function and stay abreast of modern society. Of course the supra national nature of the web, will require the need for supranational cooperation on any kind of intervention. Political intervention may quicken the pace of progress on these issues, it could also ensure that data rights and opt-out facilities are apparent and transparent to citizens. Finally, certain government measures may benefit both users and service offerings in the long term, by instilling confidence. For instance, a service like Penzu would perhaps better thrive if minimum requirements were in place, granted the details of any technical standards is a messy and arduous business. This kind of confidence, that individuals have certain assurances; would in aggregate serve to speed up adoption of existing and emerging services. It would also assure vigilance, in the face of further encroachment of the market into everyday life.
Copyright © 2006-2009 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
See; Facebook retain right to user data after account deletion
In fact, I've come to like these new online offerings so much, that I want to do more!! For instance, I've been playing around with the idea of keeping an online journal for some time now. Having chosen a service that I liked; 'Penzu' , I realised that after keeping entries for more than a week, I had no assurance as to the integrity and access to data in the event of this service ceasing. The site gave no assurance about data portability or policy with regard to cessation of service. Then, I came across this interesting article by Bill Thompson over at the BBC See article: http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/technology/7760528.stm
He rightly raised the issue of data portability concluding that web site developers should do more. (Data Portability concerns the ability for user data to be transferred to another service, or downloaded by the user.) However I think he failed to fully argue what should be done about this issue. For example, if your data and/or intellectual property resides on a free online site, and that service changes its offering; is it made transparent and simple if you decide to jump ship to another offering? If your data and/or intellectual property resides on an online website and that website goes bust, will your data be kept safe and retrievable?
We already have some national government policies in place concerning the protection, control and privacy of data to individuals. However, I feel it should also be up to government to protect citizens with regard to movement, ownership and integrity of user data. For instance, more needs to be done to ensure that website owners have a required responsibility from the outset; to provide data portability and maintain this ability even after termination of service. Perhaps, this would require that the government step in and provide servers to back up user data in the event of a company ceasing. This could be in tandem with services (new or old) being required to ensure data integrity in the case of termination of service etc. Issues like ownership of data also needs to be addressed.
It is often argued that government should not inhibit the market, but I argue that the government should steer the market, maximising the longterm interests of it's citizens. Thus, I don't see a problem with positive interference in the market. The role of government is afterall to balance the realms of life. This is in view of citizens becoming increasingly reliant on the market, and thus, on online commercial offerings to function and stay abreast of modern society. Of course the supra national nature of the web, will require the need for supranational cooperation on any kind of intervention. Political intervention may quicken the pace of progress on these issues, it could also ensure that data rights and opt-out facilities are apparent and transparent to citizens. Finally, certain government measures may benefit both users and service offerings in the long term, by instilling confidence. For instance, a service like Penzu would perhaps better thrive if minimum requirements were in place, granted the details of any technical standards is a messy and arduous business. This kind of confidence, that individuals have certain assurances; would in aggregate serve to speed up adoption of existing and emerging services. It would also assure vigilance, in the face of further encroachment of the market into everyday life.
Copyright © 2006-2009 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
See; Facebook retain right to user data after account deletion
Tuesday, January 20, 2009
Response to; I haz a Nom
A friend of mine; 'Victoria MacArthur' over at 'Propositional Structure' , today wrote an interesting muse about personal writings on blogs. In it, she put forward the question; as to how personal one should get in a blog? How much does one 'feel comfortable' with sharing on the web? And, what are the ramifications in terms of employers vetting candidates for jobs etc. ?
She seemed to raise 2 fundamental issues:
1. The question of instinctually or more cognitively wanting to protect and control one's identity.
2. The pragmatic issues around needing to negotiate one's privacy on the web.
This got me thinking about some of the key issues at stake which I've layed out as follows:
First off, there is the problem of ‘identity crime’. This is a type of crime which is on the increase and one further enabled by the web. This can occur whereby you leave enough breadcrumbs on the internet for someone to cross-correlate that information and build up a profile on you. This profile can then be used to create a false identity for another person, or even worse; to 'steal' someones identity. Outside of crime though, it may be a case that you unknowingly have left the jig-saw for an online profile of you, which can be pieced together by employers and others. Thus, you may incremently and unknowingly lose your privacy online.
Second off, identity in the 21st century has increasingly become ‘individuated’, whereby individuals construct the ’self’ through-out their lives. (Note: This construction can be conscious, unconconscious and indeed shaped with social structure at micro, meso, macro level) What’s important about posting information on the internet, is that it can leave relics of your previous ’selves’. Thus, your past can constrain your identity ‘construction’, particularly when it cannot be erased from the past. For example, archive.org has been archiving web pages on the internet for nearly 10 years now. Fragments of your past identities on the internet can be seen as both positive and negative. One positive, is that it means you have to face all of your past realities (and integrate them). On a negative, it can give people (such as employers) a false sense of who you are ‘now’; your past may constrain you in the eyes of others. It may also constrain your own sense of identity and your ability to construct.
Third Point. There is an issue with social networking sites etc., whereby individuals can have too much ‘control’ of their online identities. Individuals can now put themselves in a position to be able to package their life online, and this online construction may not be ‘holistically’ representative of the integrated identity. It may represent a planned and controlled fragment of your identity, or even an entirely consciously manufactured identity. At the other extreme, the fragments of identity that do lie on the internet, may result in people constructing a narrow and perhaps even false sense of who you are as an integrated identity.
Final point. The solution to all this seems 3 fold. (1)Government policy with regards to data protection etc. (2)Some responsibility and forsight with regard to website owners and content managers (3)Individual responsiblity, in terms of managing your online identity and maintaining a degree of foresight.
Overall, it seems like there isn’t a polarising solution. A balanced attitude to your identity and privacy on the internet seems the best approach. Individuals need to be vigilant and maintain foresight when posting information on the web. On the other-hand, individuals need to be attentive to how, ‘controlled’ and ‘representative’ that information on the web is of their ‘integrated identity’.
To see the original article, go to; http://www.victoriamacarthur.com/2009/01/20/i-haz-a-nom/
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
She seemed to raise 2 fundamental issues:
1. The question of instinctually or more cognitively wanting to protect and control one's identity.
2. The pragmatic issues around needing to negotiate one's privacy on the web.
This got me thinking about some of the key issues at stake which I've layed out as follows:
First off, there is the problem of ‘identity crime’. This is a type of crime which is on the increase and one further enabled by the web. This can occur whereby you leave enough breadcrumbs on the internet for someone to cross-correlate that information and build up a profile on you. This profile can then be used to create a false identity for another person, or even worse; to 'steal' someones identity. Outside of crime though, it may be a case that you unknowingly have left the jig-saw for an online profile of you, which can be pieced together by employers and others. Thus, you may incremently and unknowingly lose your privacy online.
Second off, identity in the 21st century has increasingly become ‘individuated’, whereby individuals construct the ’self’ through-out their lives. (Note: This construction can be conscious, unconconscious and indeed shaped with social structure at micro, meso, macro level) What’s important about posting information on the internet, is that it can leave relics of your previous ’selves’. Thus, your past can constrain your identity ‘construction’, particularly when it cannot be erased from the past. For example, archive.org has been archiving web pages on the internet for nearly 10 years now. Fragments of your past identities on the internet can be seen as both positive and negative. One positive, is that it means you have to face all of your past realities (and integrate them). On a negative, it can give people (such as employers) a false sense of who you are ‘now’; your past may constrain you in the eyes of others. It may also constrain your own sense of identity and your ability to construct.
Third Point. There is an issue with social networking sites etc., whereby individuals can have too much ‘control’ of their online identities. Individuals can now put themselves in a position to be able to package their life online, and this online construction may not be ‘holistically’ representative of the integrated identity. It may represent a planned and controlled fragment of your identity, or even an entirely consciously manufactured identity. At the other extreme, the fragments of identity that do lie on the internet, may result in people constructing a narrow and perhaps even false sense of who you are as an integrated identity.
Final point. The solution to all this seems 3 fold. (1)Government policy with regards to data protection etc. (2)Some responsibility and forsight with regard to website owners and content managers (3)Individual responsiblity, in terms of managing your online identity and maintaining a degree of foresight.
Overall, it seems like there isn’t a polarising solution. A balanced attitude to your identity and privacy on the internet seems the best approach. Individuals need to be vigilant and maintain foresight when posting information on the web. On the other-hand, individuals need to be attentive to how, ‘controlled’ and ‘representative’ that information on the web is of their ‘integrated identity’.
To see the original article, go to; http://www.victoriamacarthur.com/2009/01/20/i-haz-a-nom/
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Labels:
article,
data protection,
identity,
identity construction,
internet,
opinion,
personal,
privacy,
response
Saturday, January 03, 2009
Letting the cat back out of the bag; towards an accepted view of emancipation
Next article on emancipation, whenever I get the chance to write it, it'll be more theoretically informed than the last!!
Have a great 09!!!!
Shane
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Have a great 09!!!!
Shane
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Wednesday, December 31, 2008
"The knowing look" maneuver
Abstract
In social settings; 'the knowing look' is a particular phenomena which can be considered as part of a range of practiced social skills. It can be a subtle and at times complex phenomena forming part of the 'dance' of social interaction. It may be a more positive or times negative activity, more knowingly or unknowingly practiced by a few or multiple individuals, who may have converging or diverging motivations. It is argued that there may be conceptualised a number of motivations and effects arising with this phenomena and any number of these may combine together as 'motivations' and result in 'effects'. It is argued that providing an indepth understanding of this particular phenomena can be of benefit to professionals and individuals in becoming aware, reflective and vigilant to social situations where this and other social cues are practiced.
Introduction
The 'knowing look', commonly seen as a fleeting shared eye contact and associated facial gesture amongst two or more people, often plays a crucial role in friendship building as well as reflecting a continuing bond amongst close ties. It has been a social cue practiced by humans for generations. Manifesting as a brief gesture in the social 'dance', it is an art in itself, known by many but perhaps practiced by fewer. It's negotiation and timing are crucial in carrying it off as naturally and effortlessly as possible. It can be practiced as part of a conversation between two, or may be practiced in social settings amongst numerous individuals. It can seem an almost spontaneous occurrence arising out of a situation, or it may be more resolutely 'instigated' as an opportunity persists. It is an interesting yet under-analysed phenomena and this brings me to seek to provide a conceptual framework which can throw further light on its raison d'être, as well as to suggest some applied or normative uses from gaining a more indepth understanding. Bearing in mind 'the knowing look' arises as a specifically social phenomena, questions which have helped focus the enquiry include: What is the 'knowing look' activity? Why do people instigate the 'knowing look' activity? How did it arrise? Does it have a purpose? If so, what purpose does it serve? What are the motivations behind its 'instigation' and the effects of its practice?
Proposed conceptual framework
There appears several 'motivations' which may arise with 'the knowing look' and 'effects' which result from its practice. These can be broken down into:
1.Power and Leveraging power
2.Building friendships
3.Consolidating friendships
4.Subtle forms of bullying (ridiculing, isolating etc.)
5.Communicating an understanding, perspective or reality
6.Acknowledging shared understandings, perspective or realities
7.Solidifying understandings, perspectives or realities
8.Expressing concern
It may be the case that a combination of these concepts culminate as a complex cognitive-affective expression manifesting physically as a 'knowing look' which is then realised (either intended or unintended) as a singulation or combination of the above concepts. Importantly, it may be instigated as a more cognitive (thinking) or affective (feeling) expression, and this may be motivated at a more conscious or unconscious level. Also, it may be perscieved and reflected upon by the participants at varying degrees of consciousness. It's practice may be more learned and behavioural, or may be more consciously and contingently instigated.
Leveraging power relates to the idea that there are flows of power amongst social groupings or even perceived flows of power, where individuals consciously or otherwise seek to solidify or extend their power and related stature and influence; through participating in activities which can realise their goals. They may also seek to positively leverage the flow of power amongst a social grouping where they percieve an inbalance, or they may have whats considered negative or malicious underlying motivations. These activities can relate to physical mannerisms, as well as communicative utterances, which serve an instrumental purpose. Of course it must be recognised that there are also learned behaviours and traits as well as non-instrumental mannerisms, expressions and communication which takes place. The important point is that by participating in 'the knowing look' activity, individuals may be consciously or unconsciously seeking to leverage power within the social setting. For example, they may be looking to take (social) power away from the unknowing participant, or in tandem or otherwise, they may be seeking to relatively increase their stature and influence relative to the 'unknowing' participant. Furthermore, they may seek not necessarily to leverage power, but may seek to manifest power as a result of the social cue. The concept of power can be related closely to bullying but also to friendship formation and consolidation.
Building Friendships relates to how individuals use the particular social cue of the 'knowing look' to create or build friendships with the person participating in this activity. This can often closely relate to acknowledging shared realities, which can act as commonality on which to build friendship.
Consolidating Friendships relates to maintaining and strengthening relationships through participating in such social activities. For example, using 'the knowing look' may be an opportunity to solidify or strengthen friendship where there is a perceived weakness in the 'tie' that one wishes to address. Often the 'knowing look' activity may not be 'purposeful' or 'instrumental' as such, some times it may be more accurately envisaged as a reflection of a continuing friendship.
Bullying 'The knowing look' practiced to the exclusion of others within the particular social setting may be a form of psychological bullying. In this instance, the 'activity' or 'practice' may be purposefully or unintentionally a form of bullying. In the case of purposeful bullying; the persons participating in the 'knowing look' (particularly the instigator) may be seeking to (1)ridicule, (2)exclude, (3)isolate or (4)a combination of the first three with a malicious intent in mind. To add to this, if the 'knowing look' was meant to be witnessed by the 'victim', it may be construed as a more explicit form of bullying whereby ridicule or embarrassment etc is sought to be inflicted, or a communication of power is sought to be delivered etc. Furthermore, if the 'unknowing' participant unintentionally witnesses the act, they may be the victim of unintentional bullying. It is useful at this time to reflect on the concepts of positive exclusion (harmless) and negative exclusion (malicious). There are of course many instances of 'the knowing look' which are forms of positive exclusion. The concept of bullying is closely tied to that of Power and leveraging power, and represents leveraging power and diminishing power in a purer form (moving towards an 'ideal type') and with more negative motivations and/or effects.
Communicating understandings, perspectives and realities
The knowing look may be instigated for the specific purpose of communicating with the recipient through subtle sensorimotor behaviour. In this instance the instigator wishes to communicate an understanding, perspective or reality. This can often be used in the act of courting whereby the activity is exclusive to 2 individuals and is not concerned with a third party, but may also be used in acts of consolidating friendships, expressing concern, leveraging power or even bullying etc.
Acknowledging shared perspectives or realities
'The knowing look' is often a social cue practiced in order to acknowledge a shared reality or perspective. It may to a lesser degree entail acknowledging an 'understanding'. For example individuals may capitalise on a shared perspective or understanding for use as a commonality from which to build or consolidate a friendship or relationship. It may be instigated by one individual seeking acknowledgement for an understanding, perspective or reality to which they believe they have, or have bore witness to, or it may be a spontaneous occurrence amongst two or more individuals.
Solidifying realities or perspectives
Similar to acknowledging shared realities or perspectives, the knowing look may be about solidifying or substantiating an understanding, reality or perspective. Individuals may look for confirmation that their understanding, perspective or reality is somehow 'more real' or not merely envisioned by themselves.
Expressing concern
Finally, the Knowing look may be concerned with expressing or communicating a concern for the unknowing individual in question. This may arise as individuals bear witness to communications and behaviourisms from an individual which they 'think' they understand, or which they 'think' they don't understand. This concept is closely tied and is a common motive and effect; in communicating, acknowledging and solidifying understandings, perspectives and realities. It may range from issuing a mere bemusement with the unknowing individual to an expression of deep concern.
Conclusion and discussion
'The knowing look' activity forms as part of a range of social skills which individuals develop and participate in, known cumulatively as social competence. It arises naturally as individuals develop socially through a range of social interaction. Often degrees of social interaction need to be 'maintained' in order for individuals to 'maintain' their ability to successfully initiate and participate in social cues and etiquette's. It is proposed that there may be motivations and effects related to the practice of 'the knowing look'. These may be broken down into 8 concepts, though it must be recognised that many of these concepts are in many instances closely bound to each other, with 'bullying' and 'expressing concern' often strong and common examples of 'power and leveraging power' and 'expressing communicating undestandings etc.' respectively. Significantly, these concepts often combine as motivations and result in planned and unplanned effects. 'The knowing look', may be instigated as a more cognitive (thinking) or affective (feeling) expression, and this may be motivated at a more conscious or unconscious level. Also, it may be perscieved and reflected upon by the participants at varying degrees of consciousness. It's practice may be more learned and behavioural, or may be more consciously and contingently instigated.
It is often the case that individuals who have suffered some form of repression at some point in their lives become 'cunning' as a result of inward development. This may be seen as a 'coping strategy' and an 'attempt' to overcome the oppression (see for example Nietzsche's conscience in Ridley, 1998, p.8). Following on from this last point, there is the hypothesis that some individuals are more attentive to their social abilities and are more active in utilising certain social cues to realise their goals. For example, a recent study argued that "individuals either fearing [social] rejection or suffering actual [social] rejection show increased attention to social cues" (Bernstein et al, 208, p981). Thus, percieved or substantied types of 'repression', or what Bernstein et al coined 'social rejection'; may result in individuals being more sensitive to social cues, and perhaps practicing 'the knowing look' and other subtle social cues in social situations more than others, as well as interpreting and using these for purposes (and in ways) which differ from others. Although it seems likely that as one gets older, such aptness of social cues are developed by anyone participating in social interaction, it may be useful to pay particular attention to children who have developed these abilities faster and are more attentive to this practice more than others. Why is this the case? Conversely, those who are viewed as lacking the ability to read social cues(kinestic) and participate in them; may lack the sufficent socialisation or may suffer from a learning difficulty or disability.
Having more indepth and resonant knowledge about social cues may help enamour professionals in more easily identifing individuals who require attention or even help. For example, having the necessary indepth knowledge and awareness of social cues may provide; school teachers, councilors and other professionals with the ability to be more reflective, aware and vigilant to the phenomena taking place in social settings. This may lead them to more easily identify bullying and forms of negative exclusion. Also, to identify individuals who more actively practice such social cues and do so in certain ways, as well as identifying those who lack the necessary competences.
In an everyday context, having more in depth knowledge of such social cues may allow individuals to be more vigilant to its negative use in social settings, and may allow individuals to reflect on their own use of social cues and whether they be positive or negative.
Overall, it is considered that empirical work ought to be done to further explore the practice of this particular phenomena in various social settings. For example, under the problem of identifying repressed children, it could be considered whether certain children who use social cues in certain ways have developed this social skill more extensively out of a need to do so? Furthermore, professionals who wish to understand and positively act upon a social environment may benefit from being more receptive and reflective to the subtle and nuanced social practices which take place. Understanding the use of practices such as 'the knowing look', may uncover previously unrecognised problems in a social settting.
Bibliography
Bernstein, M et al, (2008) Adaptive Responses to Social Exclusion: Social Rejection Improves Detection of Real and Fake Smiles Psychological Science 19(10): 981-984
Ridley, A (1998) Nietsche's Conscience USA: Cornell University Press
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
In social settings; 'the knowing look' is a particular phenomena which can be considered as part of a range of practiced social skills. It can be a subtle and at times complex phenomena forming part of the 'dance' of social interaction. It may be a more positive or times negative activity, more knowingly or unknowingly practiced by a few or multiple individuals, who may have converging or diverging motivations. It is argued that there may be conceptualised a number of motivations and effects arising with this phenomena and any number of these may combine together as 'motivations' and result in 'effects'. It is argued that providing an indepth understanding of this particular phenomena can be of benefit to professionals and individuals in becoming aware, reflective and vigilant to social situations where this and other social cues are practiced.
Introduction
The 'knowing look', commonly seen as a fleeting shared eye contact and associated facial gesture amongst two or more people, often plays a crucial role in friendship building as well as reflecting a continuing bond amongst close ties. It has been a social cue practiced by humans for generations. Manifesting as a brief gesture in the social 'dance', it is an art in itself, known by many but perhaps practiced by fewer. It's negotiation and timing are crucial in carrying it off as naturally and effortlessly as possible. It can be practiced as part of a conversation between two, or may be practiced in social settings amongst numerous individuals. It can seem an almost spontaneous occurrence arising out of a situation, or it may be more resolutely 'instigated' as an opportunity persists. It is an interesting yet under-analysed phenomena and this brings me to seek to provide a conceptual framework which can throw further light on its raison d'être, as well as to suggest some applied or normative uses from gaining a more indepth understanding. Bearing in mind 'the knowing look' arises as a specifically social phenomena, questions which have helped focus the enquiry include: What is the 'knowing look' activity? Why do people instigate the 'knowing look' activity? How did it arrise? Does it have a purpose? If so, what purpose does it serve? What are the motivations behind its 'instigation' and the effects of its practice?
Proposed conceptual framework
There appears several 'motivations' which may arise with 'the knowing look' and 'effects' which result from its practice. These can be broken down into:
1.Power and Leveraging power
2.Building friendships
3.Consolidating friendships
4.Subtle forms of bullying (ridiculing, isolating etc.)
5.Communicating an understanding, perspective or reality
6.Acknowledging shared understandings, perspective or realities
7.Solidifying understandings, perspectives or realities
8.Expressing concern
It may be the case that a combination of these concepts culminate as a complex cognitive-affective expression manifesting physically as a 'knowing look' which is then realised (either intended or unintended) as a singulation or combination of the above concepts. Importantly, it may be instigated as a more cognitive (thinking) or affective (feeling) expression, and this may be motivated at a more conscious or unconscious level. Also, it may be perscieved and reflected upon by the participants at varying degrees of consciousness. It's practice may be more learned and behavioural, or may be more consciously and contingently instigated.
Leveraging power relates to the idea that there are flows of power amongst social groupings or even perceived flows of power, where individuals consciously or otherwise seek to solidify or extend their power and related stature and influence; through participating in activities which can realise their goals. They may also seek to positively leverage the flow of power amongst a social grouping where they percieve an inbalance, or they may have whats considered negative or malicious underlying motivations. These activities can relate to physical mannerisms, as well as communicative utterances, which serve an instrumental purpose. Of course it must be recognised that there are also learned behaviours and traits as well as non-instrumental mannerisms, expressions and communication which takes place. The important point is that by participating in 'the knowing look' activity, individuals may be consciously or unconsciously seeking to leverage power within the social setting. For example, they may be looking to take (social) power away from the unknowing participant, or in tandem or otherwise, they may be seeking to relatively increase their stature and influence relative to the 'unknowing' participant. Furthermore, they may seek not necessarily to leverage power, but may seek to manifest power as a result of the social cue. The concept of power can be related closely to bullying but also to friendship formation and consolidation.
Building Friendships relates to how individuals use the particular social cue of the 'knowing look' to create or build friendships with the person participating in this activity. This can often closely relate to acknowledging shared realities, which can act as commonality on which to build friendship.
Consolidating Friendships relates to maintaining and strengthening relationships through participating in such social activities. For example, using 'the knowing look' may be an opportunity to solidify or strengthen friendship where there is a perceived weakness in the 'tie' that one wishes to address. Often the 'knowing look' activity may not be 'purposeful' or 'instrumental' as such, some times it may be more accurately envisaged as a reflection of a continuing friendship.
Bullying 'The knowing look' practiced to the exclusion of others within the particular social setting may be a form of psychological bullying. In this instance, the 'activity' or 'practice' may be purposefully or unintentionally a form of bullying. In the case of purposeful bullying; the persons participating in the 'knowing look' (particularly the instigator) may be seeking to (1)ridicule, (2)exclude, (3)isolate or (4)a combination of the first three with a malicious intent in mind. To add to this, if the 'knowing look' was meant to be witnessed by the 'victim', it may be construed as a more explicit form of bullying whereby ridicule or embarrassment etc is sought to be inflicted, or a communication of power is sought to be delivered etc. Furthermore, if the 'unknowing' participant unintentionally witnesses the act, they may be the victim of unintentional bullying. It is useful at this time to reflect on the concepts of positive exclusion (harmless) and negative exclusion (malicious). There are of course many instances of 'the knowing look' which are forms of positive exclusion. The concept of bullying is closely tied to that of Power and leveraging power, and represents leveraging power and diminishing power in a purer form (moving towards an 'ideal type') and with more negative motivations and/or effects.
Communicating understandings, perspectives and realities
The knowing look may be instigated for the specific purpose of communicating with the recipient through subtle sensorimotor behaviour. In this instance the instigator wishes to communicate an understanding, perspective or reality. This can often be used in the act of courting whereby the activity is exclusive to 2 individuals and is not concerned with a third party, but may also be used in acts of consolidating friendships, expressing concern, leveraging power or even bullying etc.
Acknowledging shared perspectives or realities
'The knowing look' is often a social cue practiced in order to acknowledge a shared reality or perspective. It may to a lesser degree entail acknowledging an 'understanding'. For example individuals may capitalise on a shared perspective or understanding for use as a commonality from which to build or consolidate a friendship or relationship. It may be instigated by one individual seeking acknowledgement for an understanding, perspective or reality to which they believe they have, or have bore witness to, or it may be a spontaneous occurrence amongst two or more individuals.
Solidifying realities or perspectives
Similar to acknowledging shared realities or perspectives, the knowing look may be about solidifying or substantiating an understanding, reality or perspective. Individuals may look for confirmation that their understanding, perspective or reality is somehow 'more real' or not merely envisioned by themselves.
Expressing concern
Finally, the Knowing look may be concerned with expressing or communicating a concern for the unknowing individual in question. This may arise as individuals bear witness to communications and behaviourisms from an individual which they 'think' they understand, or which they 'think' they don't understand. This concept is closely tied and is a common motive and effect; in communicating, acknowledging and solidifying understandings, perspectives and realities. It may range from issuing a mere bemusement with the unknowing individual to an expression of deep concern.
Conclusion and discussion
'The knowing look' activity forms as part of a range of social skills which individuals develop and participate in, known cumulatively as social competence. It arises naturally as individuals develop socially through a range of social interaction. Often degrees of social interaction need to be 'maintained' in order for individuals to 'maintain' their ability to successfully initiate and participate in social cues and etiquette's. It is proposed that there may be motivations and effects related to the practice of 'the knowing look'. These may be broken down into 8 concepts, though it must be recognised that many of these concepts are in many instances closely bound to each other, with 'bullying' and 'expressing concern' often strong and common examples of 'power and leveraging power' and 'expressing communicating undestandings etc.' respectively. Significantly, these concepts often combine as motivations and result in planned and unplanned effects. 'The knowing look', may be instigated as a more cognitive (thinking) or affective (feeling) expression, and this may be motivated at a more conscious or unconscious level. Also, it may be perscieved and reflected upon by the participants at varying degrees of consciousness. It's practice may be more learned and behavioural, or may be more consciously and contingently instigated.
It is often the case that individuals who have suffered some form of repression at some point in their lives become 'cunning' as a result of inward development. This may be seen as a 'coping strategy' and an 'attempt' to overcome the oppression (see for example Nietzsche's conscience in Ridley, 1998, p.8). Following on from this last point, there is the hypothesis that some individuals are more attentive to their social abilities and are more active in utilising certain social cues to realise their goals. For example, a recent study argued that "individuals either fearing [social] rejection or suffering actual [social] rejection show increased attention to social cues" (Bernstein et al, 208, p981). Thus, percieved or substantied types of 'repression', or what Bernstein et al coined 'social rejection'; may result in individuals being more sensitive to social cues, and perhaps practicing 'the knowing look' and other subtle social cues in social situations more than others, as well as interpreting and using these for purposes (and in ways) which differ from others. Although it seems likely that as one gets older, such aptness of social cues are developed by anyone participating in social interaction, it may be useful to pay particular attention to children who have developed these abilities faster and are more attentive to this practice more than others. Why is this the case? Conversely, those who are viewed as lacking the ability to read social cues(kinestic) and participate in them; may lack the sufficent socialisation or may suffer from a learning difficulty or disability.
Having more indepth and resonant knowledge about social cues may help enamour professionals in more easily identifing individuals who require attention or even help. For example, having the necessary indepth knowledge and awareness of social cues may provide; school teachers, councilors and other professionals with the ability to be more reflective, aware and vigilant to the phenomena taking place in social settings. This may lead them to more easily identify bullying and forms of negative exclusion. Also, to identify individuals who more actively practice such social cues and do so in certain ways, as well as identifying those who lack the necessary competences.
In an everyday context, having more in depth knowledge of such social cues may allow individuals to be more vigilant to its negative use in social settings, and may allow individuals to reflect on their own use of social cues and whether they be positive or negative.
Overall, it is considered that empirical work ought to be done to further explore the practice of this particular phenomena in various social settings. For example, under the problem of identifying repressed children, it could be considered whether certain children who use social cues in certain ways have developed this social skill more extensively out of a need to do so? Furthermore, professionals who wish to understand and positively act upon a social environment may benefit from being more receptive and reflective to the subtle and nuanced social practices which take place. Understanding the use of practices such as 'the knowing look', may uncover previously unrecognised problems in a social settting.
Bibliography
Bernstein, M et al, (2008) Adaptive Responses to Social Exclusion: Social Rejection Improves Detection of Real and Fake Smiles Psychological Science 19(10): 981-984
Ridley, A (1998) Nietsche's Conscience USA: Cornell University Press
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Sunday, December 07, 2008
Shame on you Chris Martin, Shame
The artist Joe Satriani is rightly suing coldplay for blatant plagiarising his work, as demonstrated on the single 'viva la vida'.
Joe Satriani - if i could fly:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CMcjXo8ZuqE
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Joe Satriani - if i could fly:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CMcjXo8ZuqE
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Labels:
coldplay,
joe satriani,
plagiarism,
suing,
viva la diva
Wednesday, December 03, 2008
Ubuntu grievances....
So I'm back using Ubuntu (the fancy gui laden linux), literally because Vista's lackluster performance led me to.
And yes, what a relief; speed, performance and it's cracking GUI advanced interface options come as a welcome relief. But, ubuntu obviously has its shortcomings, the most noticably so far being installing items. Basically, if you have the update manager running to download an upgrade or several program updates; you can't install anything else simulataneously. Furthermore, you can only install one item at a time. This can be especially frustrating given upgrades can take hours to download on an average ISP connection.
Also, Vista's 'Cleartype', 'graphics', 'icons' and 'font' choices are still miles ahead of Ubuntu and customising these items is a must in order not to feel like you've been transported to the past!
Finally, concluding my brief rant, the gdesktop widgets are still wanting in many regards and thus, on my 'wishlist', would be a plethora of new widgets to choose from. But overall, gripes are superficial at worst, Ubuntu has evolved in leaps and bounds since I got involved 2 years ago!
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
And yes, what a relief; speed, performance and it's cracking GUI advanced interface options come as a welcome relief. But, ubuntu obviously has its shortcomings, the most noticably so far being installing items. Basically, if you have the update manager running to download an upgrade or several program updates; you can't install anything else simulataneously. Furthermore, you can only install one item at a time. This can be especially frustrating given upgrades can take hours to download on an average ISP connection.
Also, Vista's 'Cleartype', 'graphics', 'icons' and 'font' choices are still miles ahead of Ubuntu and customising these items is a must in order not to feel like you've been transported to the past!
Finally, concluding my brief rant, the gdesktop widgets are still wanting in many regards and thus, on my 'wishlist', would be a plethora of new widgets to choose from. But overall, gripes are superficial at worst, Ubuntu has evolved in leaps and bounds since I got involved 2 years ago!
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Wednesday, October 15, 2008
Bye Bye Paper ??
Now that e-readers and e-paper are finally beginning to trickle into the market-place, what are the key issues surrounding these developments and where could this all lead?
It's now been 2 years since the second generation of E-Reader devices hit the market. The past year has seen several additions to the line-up including; Amazon's Kindle and an updated Sony E-Reader. These devices may herald the transformation of the publishing industry, as e-books can be downloaded and updated with these devices, consumer's and scholar's can effectively have their book collection or more significantly the world's libraries on the palm of their hand's.
What's so 'special' and significant about these devices is the incorporation of 'E-Ink' displays. E-Ink, unlike LCD or LED displays, are not back-lit. A kind of 'electronic ink' gets rearranged to form words and pictures as the user switches pages. The technology allows improved readability and reduced eye-strain, in addition to much improved battery life as compared to LCD. The technology promises to marry many of the benefits of a traditional book with the advantages of computers and the Web.
Now that the technology has gone to industrial scale production and sales are 'slowly' creeping up, the market is forming to allow further innovation, proliferation and price reduction. In essence, the cogs in the E-ink machine are slowly beginning to turn. Just recently, a German factory in Dresden (Plastic Logic), went into operation turning out a 'newspaper' version of the technology alongside the 'EBook Reader' devices already in 'circulation'. These devices’s, (the technology still in its infancy), will eventually supplement, and may one-day even replace traditional newspapers. Developing technology and industry growth in this sector means we may inhabit a predominantly 'paperless' world in the not too distant future. A world in some ways reminiscent of that portrayed in Spielberg's film, 'Minority Report'. The devices 'currently' are only available in black and white, other short-comings currently exist such as memory, processing power, battery life and connectivity. However, down the road, it is envisaged that such devices will form part of the 'ubiquitous' web, with multi-coloured screens, multi-media capability and live updating of content. Furthermore, the amount of content and functionality of these E-Reader devices will drastically improve. The latest generation already allow for underlining and note taking of text, in the not too distant future, continual updating of e-books, user's contributing through discussion of passages, as well as enhanced functionality such as automatic summarisation and correlation of note-taking etc, will undoubtedly be forthcoming.
There are a few significant issues which ought to be explored in light of this. Firstly, how environmentally sustainable will such an industry be, as opposed to the paper industry? What will the total environmental footprint be in manufacturing and disposing of these devices? We have already seen from existing computer and electronic manufacturing, that this footprint can be significant. Hundreds of parts, manufactured using harmful chemicals, flown in from around the world to an assembly site before being shipped back around the world; represents industry norms at present. This is before we factor in direct and indirect energy, water and waste by-products. We must also question the short life-cycle of these devices (in a capitalist society) as well as their disposal and replacement. In sum, there is the need to scrutinise and improve the environmental credentials of the electronics industry from cradle to grave. The European WEEE (waste electrical and electronic equipment) directive goes some way to steering the industry in a positive direction.
Certainly the traditional paper industry has environmental shortfalls with much room for improvement. Even with the growth of E-Paper replacing paper, it must be recognised that packaging presently consumes half of all paper produced. Up to 40 of total municipal waste in the US is paper based. Paper production has been cited as accounting from anything between 20% to 40% of global logging and is one of the most water intensive industries requiring c.20 thousand gallons of water per ton of paper. Concern also exists about the degree of wood logging from non-'farmed' forests, particularly in developing countries. This is in light of global paper consumption increasing at over 3% annually into the foreseeable future. On a positive note, recycled paper accounts for about c.40% of total paper used globally, though in some western countries; recycling rates have hit 60%. Thus, there is enormous scope for overall improvements in paper recycling, and in reduction of packaging. With the advent of e-paper, significant environmental benefits may be added by reducing paper use, if an environmentally sustainable electronics industry emerges to supplement it. One that in aggregate outweighs the benefits of recycled paper. In any event, the push and pull factors of e-paper and e-readers looks set to increase!!
There are also other issues that must be considered alongside environmental concerns. Advertising currently subsidises the newspaper industry, can a model be developed that ensures the devices themselves are subsidised so that the gap in information inequality is not increased? Technology has the potential to increase equality by improving access to more information by all sectors in society, but without foresight, technology can also act as a barrier in terms of cost, awareness, understanding and 'computer literacy'.
We must also ask whether more information is better information or even needed information. Are we becoming a society of superficial information junkies? Research has shown we increasingly 'flicker' through content rapidly on the internet, prepared to trawl through a number of articles in order to grab snippets of interesting or relevant information without spending the time trying to get a more in-depth understanding of particular topics. The emergence of E-paper devices may continue and expand this trend for better or worse. With such an abundance of easily retrieval information available, it may seem increasingly difficult for individuals to 'filter' and 'process' the abundance of information. Thus, how will all this impact us psychologically in terms of attention span, memory and behavioural traits? There is belief that it will lead to increased selectivity and 'differentiation', meaning readers can increasingly become selective about what content they wish to know about, perhaps at the expense of democracy and the 'public good'. It is a well known phenomenon that individuals have a tendency to selectivity, choosing information that's agreeable with their prior knowledge, sometimes adopting theories about things which favour preconceived biases or conclusions. Existing Paper formats cover a wide range of content from politics, social issues to economic and lifestyle issues. Individuals 'paying' for a newspaper may be more inclined to read from a wider range of stories and view-points, in-turn having a more rounded knowledge of current-affairs and everyday reality as a result. With E-Paper, users will eventually be able to choose what content (and by whom) they wish to receive by page or even by column. Thus, research which ascertains the information behaviour of e-paper users seems timely.
Ending on a positive note, the maturation of e-reader devices may have enormous benefits for scholars and consumers alike. It certainly means increased access and availability of high quality content. With access through a library portal, students will no-longer need to visit the library for text books; there will be no such thing as limited availability. There will be enormous easing of 'friction' in terms of time and space, as books become almost instantaneously retrievable, illiminating the time and journey involved in accessing content. Furthermore, unlike books on a shelf, e-books don't degrade and can't be defaced. Students and consumers may have automatic updates; newer editions may be factored into the 'purchase' or 'rental' price of content. With online accounts, e-readers that get lost or stolen will not mean the need for repurchasing of content. From this we can gage that the role of the traditional library may change in light of this new model. The issue of 'trust' may become more crucial as 'library portals' and 'publishers' (being gatekeepers of information) may be viewed increasingly like brands, some 'brands' trusted more in terms of providing filtered reliable high quality content.
Finally, where does this leave the traditional book, newspaper and magazines? Notwithstanding the likely negatives in terms of cost and environmental credentials of the paper industry, it seems likely that paper will continue to play a role in our lives long into the future. The vast proportion of information may become solely electronic but; key texts, magazines and fictional works will likely remain in print as well as electronic format. Changes in the academic journal sector in the past 20 years indicate such a possible scenario. Individuals will likely still place emotional value on physical copy. Filled book-shelves may be an expression of personality, an indication of status, or provide a feeling of tangible ownership. The feel and smell of the book, the linear arrangement of text, the ability to personalise, flick through pages; all these unique features are known to aid memory. Books can also provide spatial reference and association of information, provide emotional comfort and value, as well as convey a sense of permanence. Thus, the future it seems may be principally electronic, but reports of the traditional newspaper or book’s death, are greatly exaggerated!!
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
It's now been 2 years since the second generation of E-Reader devices hit the market. The past year has seen several additions to the line-up including; Amazon's Kindle and an updated Sony E-Reader. These devices may herald the transformation of the publishing industry, as e-books can be downloaded and updated with these devices, consumer's and scholar's can effectively have their book collection or more significantly the world's libraries on the palm of their hand's.
What's so 'special' and significant about these devices is the incorporation of 'E-Ink' displays. E-Ink, unlike LCD or LED displays, are not back-lit. A kind of 'electronic ink' gets rearranged to form words and pictures as the user switches pages. The technology allows improved readability and reduced eye-strain, in addition to much improved battery life as compared to LCD. The technology promises to marry many of the benefits of a traditional book with the advantages of computers and the Web.
Now that the technology has gone to industrial scale production and sales are 'slowly' creeping up, the market is forming to allow further innovation, proliferation and price reduction. In essence, the cogs in the E-ink machine are slowly beginning to turn. Just recently, a German factory in Dresden (Plastic Logic), went into operation turning out a 'newspaper' version of the technology alongside the 'EBook Reader' devices already in 'circulation'. These devices’s, (the technology still in its infancy), will eventually supplement, and may one-day even replace traditional newspapers. Developing technology and industry growth in this sector means we may inhabit a predominantly 'paperless' world in the not too distant future. A world in some ways reminiscent of that portrayed in Spielberg's film, 'Minority Report'. The devices 'currently' are only available in black and white, other short-comings currently exist such as memory, processing power, battery life and connectivity. However, down the road, it is envisaged that such devices will form part of the 'ubiquitous' web, with multi-coloured screens, multi-media capability and live updating of content. Furthermore, the amount of content and functionality of these E-Reader devices will drastically improve. The latest generation already allow for underlining and note taking of text, in the not too distant future, continual updating of e-books, user's contributing through discussion of passages, as well as enhanced functionality such as automatic summarisation and correlation of note-taking etc, will undoubtedly be forthcoming.
There are a few significant issues which ought to be explored in light of this. Firstly, how environmentally sustainable will such an industry be, as opposed to the paper industry? What will the total environmental footprint be in manufacturing and disposing of these devices? We have already seen from existing computer and electronic manufacturing, that this footprint can be significant. Hundreds of parts, manufactured using harmful chemicals, flown in from around the world to an assembly site before being shipped back around the world; represents industry norms at present. This is before we factor in direct and indirect energy, water and waste by-products. We must also question the short life-cycle of these devices (in a capitalist society) as well as their disposal and replacement. In sum, there is the need to scrutinise and improve the environmental credentials of the electronics industry from cradle to grave. The European WEEE (waste electrical and electronic equipment) directive goes some way to steering the industry in a positive direction.
Certainly the traditional paper industry has environmental shortfalls with much room for improvement. Even with the growth of E-Paper replacing paper, it must be recognised that packaging presently consumes half of all paper produced. Up to 40 of total municipal waste in the US is paper based. Paper production has been cited as accounting from anything between 20% to 40% of global logging and is one of the most water intensive industries requiring c.20 thousand gallons of water per ton of paper. Concern also exists about the degree of wood logging from non-'farmed' forests, particularly in developing countries. This is in light of global paper consumption increasing at over 3% annually into the foreseeable future. On a positive note, recycled paper accounts for about c.40% of total paper used globally, though in some western countries; recycling rates have hit 60%. Thus, there is enormous scope for overall improvements in paper recycling, and in reduction of packaging. With the advent of e-paper, significant environmental benefits may be added by reducing paper use, if an environmentally sustainable electronics industry emerges to supplement it. One that in aggregate outweighs the benefits of recycled paper. In any event, the push and pull factors of e-paper and e-readers looks set to increase!!
There are also other issues that must be considered alongside environmental concerns. Advertising currently subsidises the newspaper industry, can a model be developed that ensures the devices themselves are subsidised so that the gap in information inequality is not increased? Technology has the potential to increase equality by improving access to more information by all sectors in society, but without foresight, technology can also act as a barrier in terms of cost, awareness, understanding and 'computer literacy'.
We must also ask whether more information is better information or even needed information. Are we becoming a society of superficial information junkies? Research has shown we increasingly 'flicker' through content rapidly on the internet, prepared to trawl through a number of articles in order to grab snippets of interesting or relevant information without spending the time trying to get a more in-depth understanding of particular topics. The emergence of E-paper devices may continue and expand this trend for better or worse. With such an abundance of easily retrieval information available, it may seem increasingly difficult for individuals to 'filter' and 'process' the abundance of information. Thus, how will all this impact us psychologically in terms of attention span, memory and behavioural traits? There is belief that it will lead to increased selectivity and 'differentiation', meaning readers can increasingly become selective about what content they wish to know about, perhaps at the expense of democracy and the 'public good'. It is a well known phenomenon that individuals have a tendency to selectivity, choosing information that's agreeable with their prior knowledge, sometimes adopting theories about things which favour preconceived biases or conclusions. Existing Paper formats cover a wide range of content from politics, social issues to economic and lifestyle issues. Individuals 'paying' for a newspaper may be more inclined to read from a wider range of stories and view-points, in-turn having a more rounded knowledge of current-affairs and everyday reality as a result. With E-Paper, users will eventually be able to choose what content (and by whom) they wish to receive by page or even by column. Thus, research which ascertains the information behaviour of e-paper users seems timely.
Ending on a positive note, the maturation of e-reader devices may have enormous benefits for scholars and consumers alike. It certainly means increased access and availability of high quality content. With access through a library portal, students will no-longer need to visit the library for text books; there will be no such thing as limited availability. There will be enormous easing of 'friction' in terms of time and space, as books become almost instantaneously retrievable, illiminating the time and journey involved in accessing content. Furthermore, unlike books on a shelf, e-books don't degrade and can't be defaced. Students and consumers may have automatic updates; newer editions may be factored into the 'purchase' or 'rental' price of content. With online accounts, e-readers that get lost or stolen will not mean the need for repurchasing of content. From this we can gage that the role of the traditional library may change in light of this new model. The issue of 'trust' may become more crucial as 'library portals' and 'publishers' (being gatekeepers of information) may be viewed increasingly like brands, some 'brands' trusted more in terms of providing filtered reliable high quality content.
Finally, where does this leave the traditional book, newspaper and magazines? Notwithstanding the likely negatives in terms of cost and environmental credentials of the paper industry, it seems likely that paper will continue to play a role in our lives long into the future. The vast proportion of information may become solely electronic but; key texts, magazines and fictional works will likely remain in print as well as electronic format. Changes in the academic journal sector in the past 20 years indicate such a possible scenario. Individuals will likely still place emotional value on physical copy. Filled book-shelves may be an expression of personality, an indication of status, or provide a feeling of tangible ownership. The feel and smell of the book, the linear arrangement of text, the ability to personalise, flick through pages; all these unique features are known to aid memory. Books can also provide spatial reference and association of information, provide emotional comfort and value, as well as convey a sense of permanence. Thus, the future it seems may be principally electronic, but reports of the traditional newspaper or book’s death, are greatly exaggerated!!
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Monday, September 29, 2008
Real Palin interview versus Saturday Night Live
Like many who caught the latest Palin sketch on Youtube, I was both highly entertained and shocked by the uncannyness of the impressions and the content of the sketches. But, whats even more shocking is how similar the sketch is to the real interview in both content and form;
Check out the sketch first at;
http://www.nbc.com/Saturday_Night_Live/video/clips/couric-palin-open/704042/
Now have a look at clips from the real interview;
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=txfqWzGMgmY
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nokTjEdaUGg&feature=related
I think the clips speak for themselves....
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Check out the sketch first at;
http://www.nbc.com/Saturday_Night_Live/video/clips/couric-palin-open/704042/
Now have a look at clips from the real interview;
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=txfqWzGMgmY
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nokTjEdaUGg&feature=related
I think the clips speak for themselves....
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Labels:
funny,
sarah palin,
saturday night live,
sketch,
tina fey,
youtube
Tuesday, September 16, 2008
Youtube funnies to check out!
Here are three youtube videos that have come my way recently...
The first is an uncanny and hilarious impersonation of Sarah Palin on 'Saturday Night Live';
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PXvbwiXqQm8
The next came to me from a friend after my Kraftwerk gig on saturday night;
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XXNZ4BntQN4&feature=related
and finally, thanks to my favourite secretary, check out this bizarre 'Ninja Cat' video;
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=muLIPWjks_M
Enjoy!!
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
The first is an uncanny and hilarious impersonation of Sarah Palin on 'Saturday Night Live';
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PXvbwiXqQm8
The next came to me from a friend after my Kraftwerk gig on saturday night;
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XXNZ4BntQN4&feature=related
and finally, thanks to my favourite secretary, check out this bizarre 'Ninja Cat' video;
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=muLIPWjks_M
Enjoy!!
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Labels:
funny,
hilary clinton,
kraftwerk,
ninja cat,
parody,
sarah palin,
sketch,
youtube
Monday, September 08, 2008
A musical tribute to RTE Newscasters....
Check out this bizarre musical tribute site to RTE newscasters:
http://www.myspace.com/songsaboutrtenewscasters
Worth a listen, but quickly becomes old and irritating....
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
http://www.myspace.com/songsaboutrtenewscasters
Worth a listen, but quickly becomes old and irritating....
Copyright © 2006-2008 Shane McLoughlin. This article may not be resold or redistributed without prior written permission.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)